B-52 Stratofortress The Legend
The B-52 Stratofortrees or the BUFF (Big Ugly Fat F#ucker), Heavy, Monkeyknocker and Coconutknocker to name a few is perhaps the most widely used and oldest of heavy strategic bombers in the United States military and the history of the US Air Force. It is also widely known that multiple generations of Americans have served in the same air frames a trait not common with US Military aircraft. This bird is unique and exceptional.
THE LEGEND!
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) since the 1950s. The bomber is capable of carrying up to 70,000 pounds (32,000 kg) of weapons, and has a typical combat range of more than 8,800 miles (14,080 km) without aerial refueling.
Beginning with the successful contract bid in June 1946, the B-52 design evolved from a straight wing aircraft powered by six turboprop engines to the final prototype YB-52 with eight turbojet engines and swept wings. The B-52 took its maiden flight in April 1952. Built to carry nuclear weapons for Cold War-era deterrence missions, the B-52 Stratofortress replaced the Convair B-36. A veteran of several wars, the B-52 has dropped only conventional munitions in combat. The B-52’s official name Stratofortress is rarely used; informally, the aircraft has become commonly referred to as the BUFF (Big Ugly Fat Fucker).
The B-52 has been in active service with the USAF since 1955. As of December 2015, 58 were in active service with 18 in reserve. The bombers flew under the Strategic Air Command (SAC) until it was disestablished in 1992 and its aircraft absorbed into the Air Combat Command (ACC); in 2010 all B-52 Stratofortresses were transferred from the ACC to the newly created Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). Superior performance at high subsonic speeds and relatively low operating costs have kept the B-52 in service despite the advent of later, more advanced aircraft, including the canceled Mach 3 B-70 Valkyrie, the variable-geometry B-1 Lancer, and the stealth B-2 Spirit. The B-52 completed sixty years of continuous service with its original operator in 2015. After being upgraded between 2013 and 2015, it is expected to serve into the 2040s.The B-52s will reach the end of their service lives by 2045, will be replaced by B-21 Raiders. (Source – Wikipedia)
ADAPTABILITY! 18 THINGS YOU MIGHT NOT KNOW ABOUT THE B-52!
1) The B-52’s very first flight was April 15, 1952 – over 64 years ago.

2) The B-52 Stratofortress was engineered to carry nuclear weapons during the Cold War, but it has only carried conventional ordnance into combat.

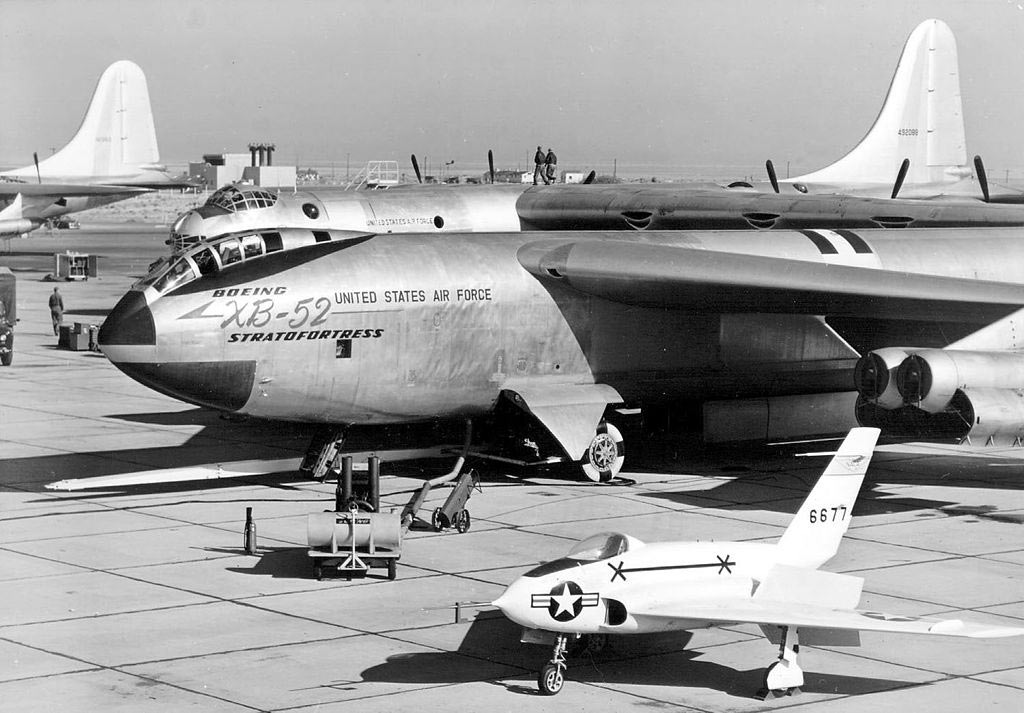
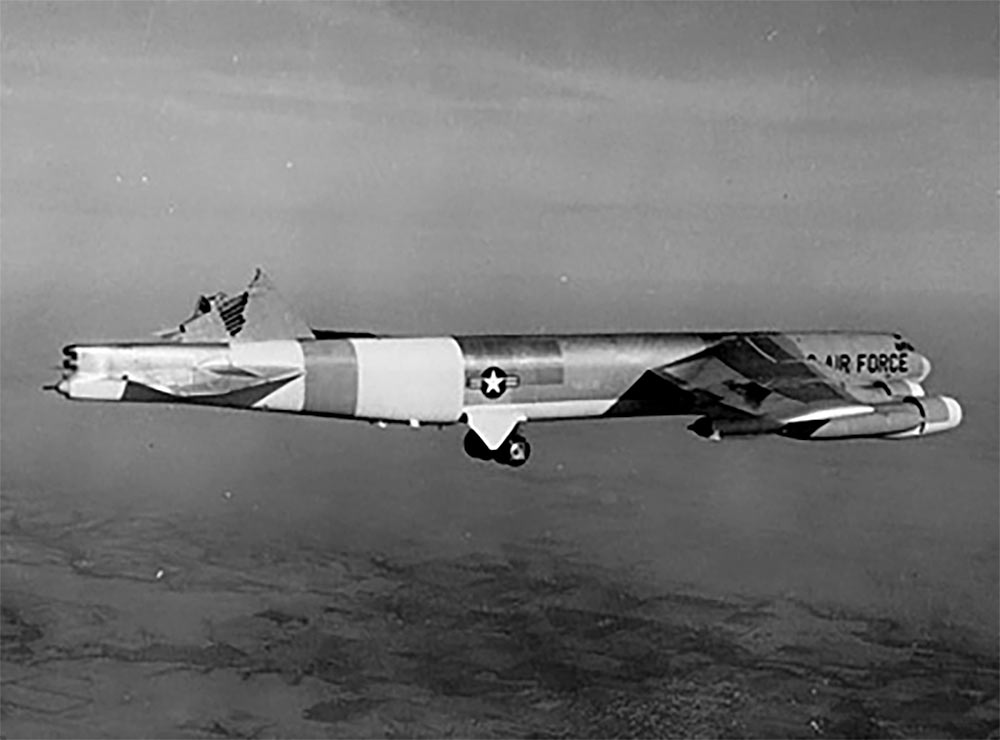
3) There were enormous improvements in aviation happening when the B-52 was first being designed, and it went through 6 major redesigns during its 5 year design period. The YB-52 pictured below was the second-to-last major redesign.
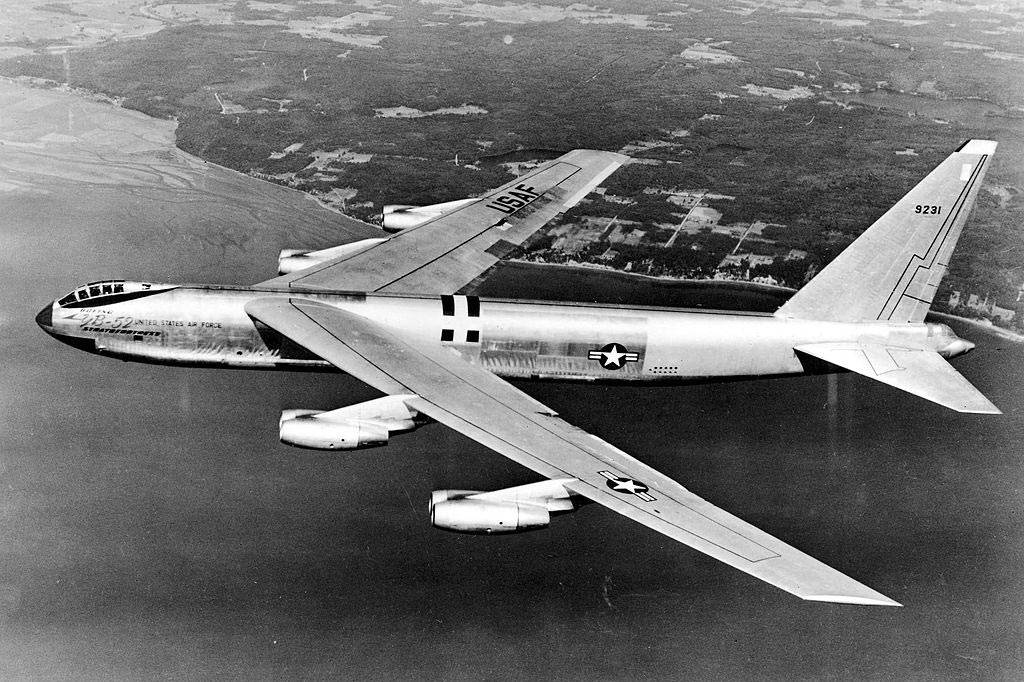

4) A B-52A Stratofortress was used to carry the USAF North American X-15. The X-15 aircraft achieved the record for fastest manned powered aircraft, with a speed of Mach 6.72.

5) Over its life there have been 744 B-52s built, but presently there are only 85 in active service, with 9 in reserve.

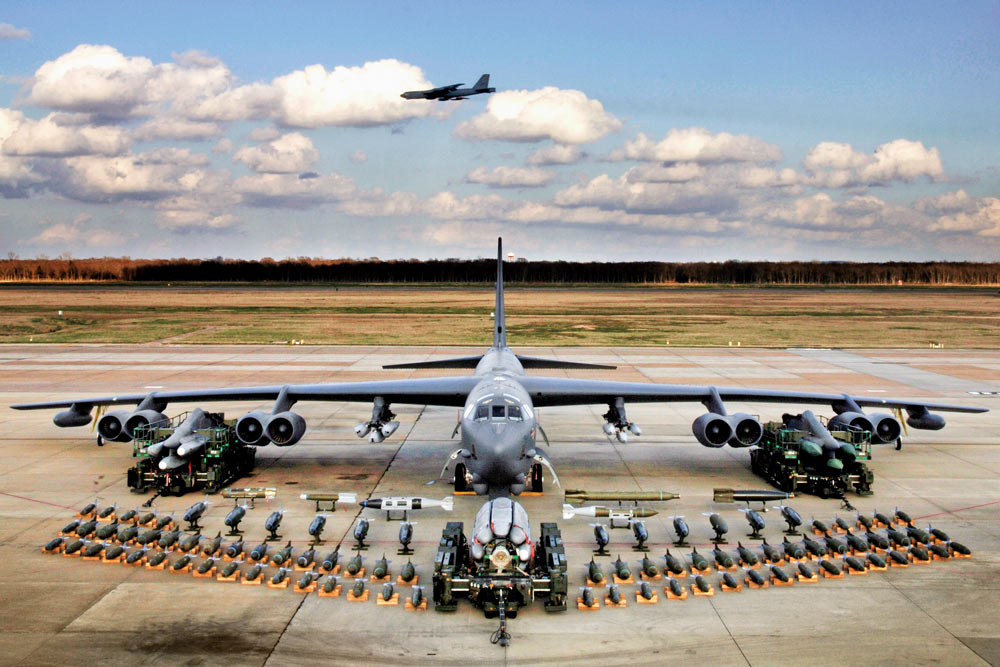
6) The B-52 Stratofortress can carry up to 70,000 pounds of ordnance which is the equivalent of 30 fully-loaded Cessna 172s. That is 35,000 tons to put it in perspective.

7) She is both young and old. B52 production ended in 1962, which means the youngest B-52 is 53 years old. Can you believe it?

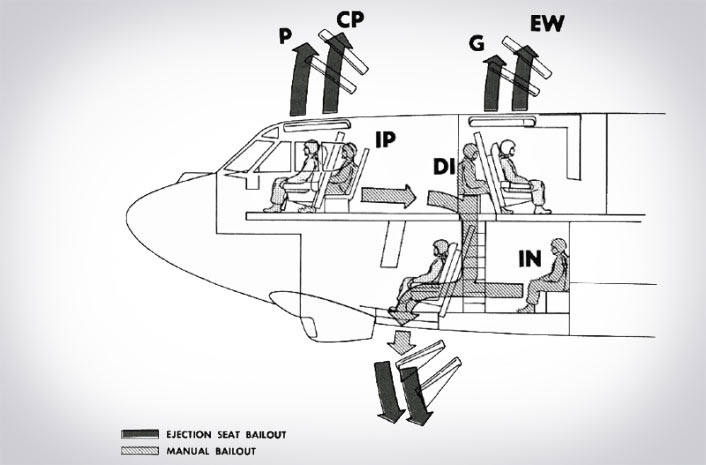
8) The B-52 Bomber has a very unique ejection system; the lower deck crew eject downward. They go north and south.
9) The B-52 is expected to remain in service until the 2040s. That’s over 90 years of service. A proud and distinct heritage of flight and service.

10) In the year 1964, a B-52 configured as a testbed to investigate structural failures flew through severe chop, shearing off its vertical stabilizer. The aircraft was still able to continue flying, and landed safely. A fortress indeed.

11) The aircraft’s navigator and radar navigator sit in the lower deck and part of the aircraft. These are the two seats that eject downward which is rare among aircraft.

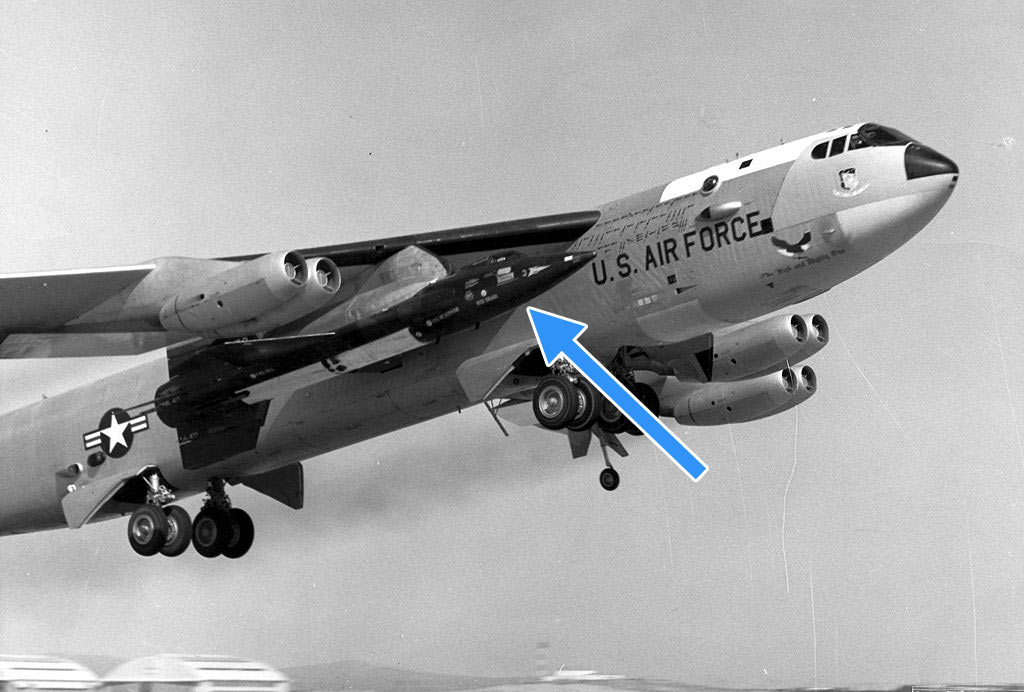
12) To comply with the SALT II Treaty requirements, cruise missile-capable aircraft had to be identifiable by spy satellites. Sure let’s tell you exactly where they are at! To comply, the B-52 “G” models were modified with a curved wing root fairing.

13) Early models of the B-52s had cabin temperature problems; the upper-deck would get hot, because it was heated by the sun, while the navigation crew would sit on the freezing fuselage floor.

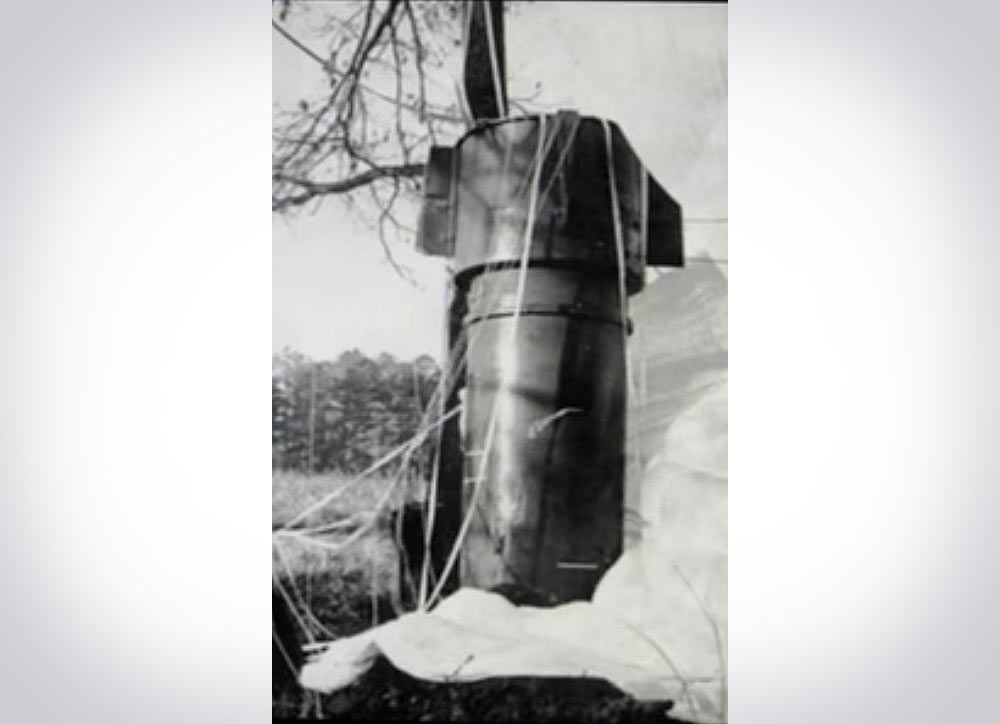
14) In 1961, a B-52G type broke up in midair over Goldsboro, NC. Two nuclear bombs on board the aircraft were in fact dropped in the process, but didn’t detonate. After the bombs were recovered, the US Air Force found that five of the six stages of the arming sequence had been completed.

15) In 1972, B-52 tail-gunner Albert Moore shot down a MiG-21 over Vietnam. It was the last recorded bomber-gunner to shoot down an enemy aircraft.

16) After the USSR fell in 1991, 365 B-52s were destroyed under the START treaty. The aircraft were stripped of usable parts, chopped into 5 pieces with a 13,000 pound steel blade, and sold for scrap at 12 cents per pound. Someone made a killing!

17) During Operation Desert Storm, B-52s delivered 40% of the weapons dropped from the air. They were there and they were on target!

18) Currently, B-52s cost $70,000 per flight hour to operate. And while they might be ugly, they’re still a pretty amazing and adaptable aircraft. No question about it.

CARPET BOMBING!
Performance * Maximum speed: 560 knots (650 mph, 1,000 km/h) * Combat radius: 4,480 mi (3,890 nm, 7,210 km) * Ferry range: 11,000 mi (8,099 nm, 15,000 km) * Service ceiling: 55,773 ft (17,000 m) * Rate of climb: 6270 ft/min[9] (m/s) * Wing loading: 30 lb/ft² (150 kg/m) * Thrust/weight: 0.51 * Lift-to-drag ratio: 21.5 (estimated) (Source – Youtube)

